

With extensive training, experience, and dedication to patient care, Dr. Deepak Chhabra, a leading Liver Cancer Doctor in Mumbai, offers comprehensive services tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual.
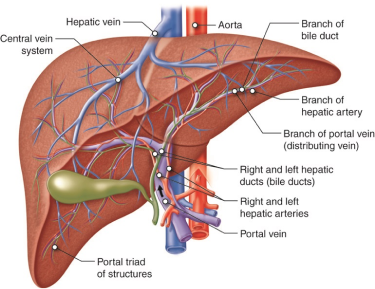
The largest organ in your abdomen is the liver. On the right side of your body, it is behind your ribs.The liver gets its supply of blood from two vessels. Most of its blood comes from the portal vein. The rest comes from the hepatic artery.
When normal liver cells become abnormal and grow too quickly, cancer develops. A tumor is a mass of abnormal cells in the liver. Malignant (cancer) tumors have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Hepatocytes, or liver cells, are where most primary liver cancers begin. Hepatocellular carcinoma or hepatoma is the name given to this kind of cancer.
metastasis.
It’s normal to wonder what might have caused cancer when you get a diagnosis. It’s not always clear to doctors why one person develops liver cancer while another does not. However, we do know that certain risk factors may make some people more likely to develop liver cancer than others.
All of the aforementioned risk factors harm liver cells and replace them with scar tissue, resulting in a bumpy, nodular liver. Almost all cases of liver cancer occur in people who first developed cirrhosis, typically as a result of hepatitis B or C infection or excessive alcohol consumption.
A factor that could make you more likely to get a disease is called a risk factor. The following risk factors for liver cancer have been identified by studies:

Frequently, early liver cancer does not manifest symptoms. At the point when the disease develops bigger, individuals might see at least one of these normal side effects.
A lump or heaviness in the upper abdomen , Swollen abdomen (bloating), Loss of appetite and feelings of fullness, Weight loss, Weakness or feeling very tired, Nausea and vomiting, Yellow skin and eyes, pale stools, and dark urine from jaundice Fever.
If you’re browsing this site without a liver cancer diagnosis, note that many symptoms are nonspecific and may stem from various conditions. Consult your primary care physician if any persist for proper evaluation.

Pain in the upper abdomen on the right side can indicate conditions like gallstones, liver inflammation, or pancreatitis, requiring medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Reasons for abdominal swelling. The cancer’s spread may cause the liver to expand. Swelling over the right side of your abdomen may result from this. Or, a buildup of fluid can lead to generalized abdominal swelling known as Ascites.

A lump or feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen may suggest issues such as an enlarged liver, abdominal hernia, or tumors, necessitating assessment by a healthcare provider.

Loss of appetite, feelings of fullness, and unexplained weight loss are common symptoms of various conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders or cancers, warranting medical attention to determine the underlying cause.

Weakness, fatigue, fever, nausea, and vomiting can indicate infections, systemic illnesses, or organ dysfunction, requiring prompt medical evaluation to identify and manage the underlying condition.

Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), pale stools, and dark urine often indicate liver or bile duct problems such as hepatitis, gallstones, or pancreatic cancer, necessitating urgent medical assessment for diagnosis and treatment.

Years of experience in treating cancer patients and participating in clinical trials have helped doctors refine liver cancer treatment in Mumbai, ensuring the most effective treatments for each type and stage of the disease.
Surgery, ablation, chemo-embolization, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy are all options for liver cancer patients. Frequently, multiple treatments may be required.
At this time, liver cancer can only be cured if discovered early & if the patient is healthy enough to undergo surgery. Other treatments may be able to help people who are unable to have surgery live longer and feel better.
The most common tests are listed here. Your doctor will choose the tests that will provide the most information about the tumor or disease. Not all of the tests need to be done.
This test can be one of the first ones done to see if there is a problem with the liver and gives an idea of how it looks.
Your doctor will check your liver, spleen, and other nearby organs for any lumps or changes in their size or shape. Additionally, ascites, an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, is examined by your doctor. Your eyes and skin may also be examined for signs of jaundice.
A CT scan is an x-ray that shows your body’s organs and structures, including any tumors. It is used to examine a cancer in greater detail and its relationship to your body’s surrounding organs. Additionally, it provides data on the spread of cancer.
Similar to a CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) creates images of your abdomen’s organs using magnetism rather than x-rays. Like a CT check, X-ray is effortless and the attraction is innocuous.
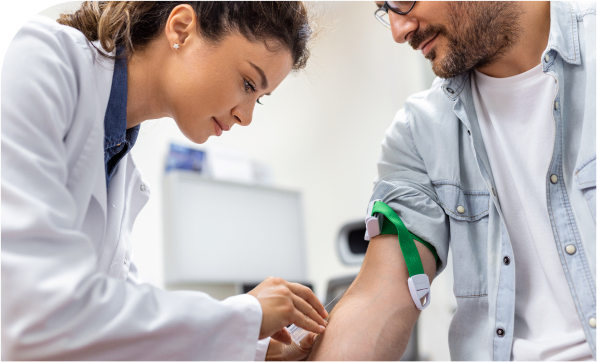
Blood tests will include AFP (alphafetoprotein), a specific tumor marker test, in addition to haemoglobin and liver function tests. This blood test looks for a substance (AFP) that liver cancer cells produce in large quantities. Additionally, markers for the viral infections Hepatitis B and C may be examined. Anti-HCV and HBsAg). If the doctors think the tumor is coming from the bile ducts or gallbladder rather than the liver cells, they may order a Ca19-9 blood test.
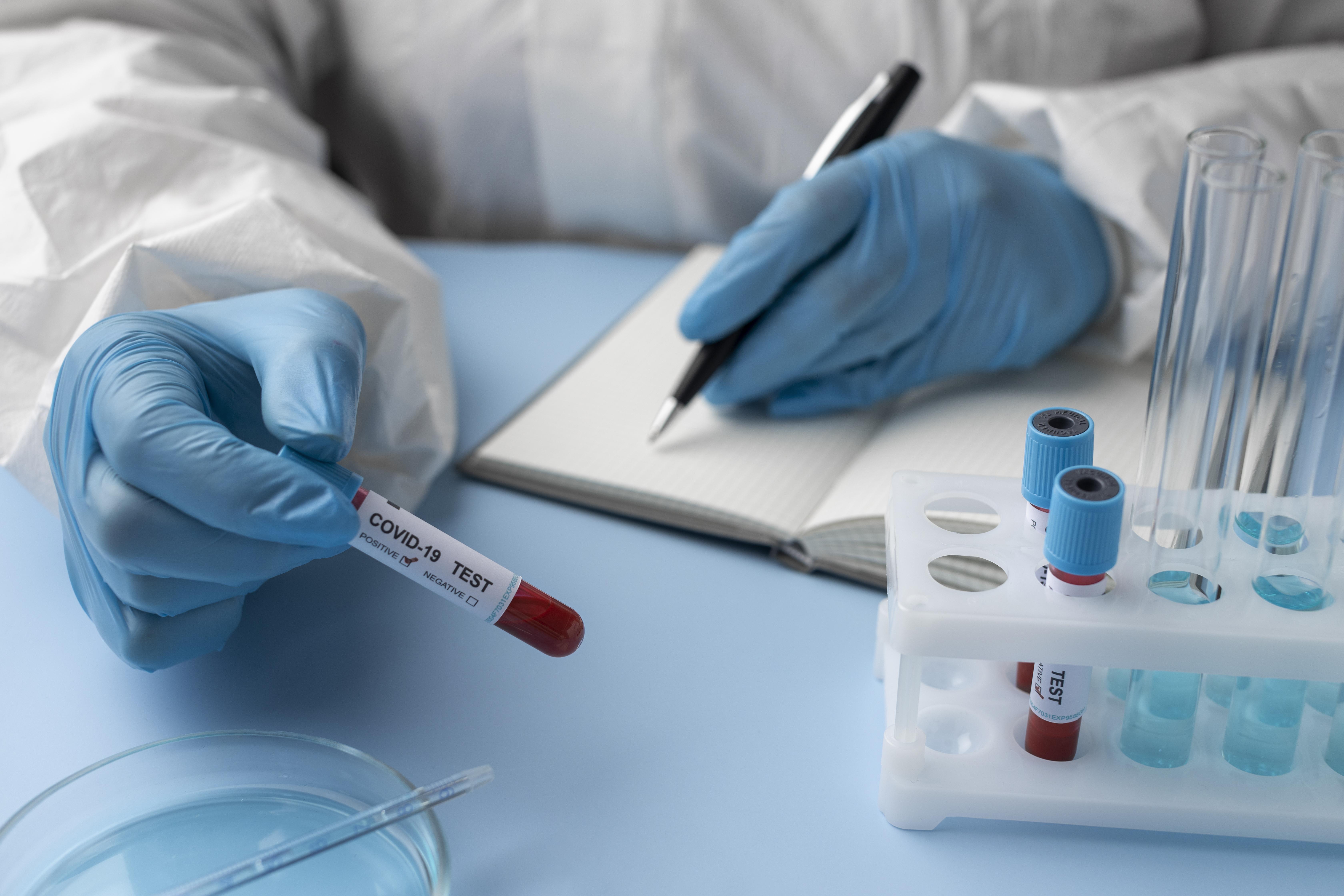
A biopsy is when a pathologist uses a small amount of tissue taken from an abnormally found area or lump to make a diagnosis under a microscope. Although a biopsy is not always necessary to diagnose liver cancer, the doctor may remove a tissue sample that can be examined under a microscope in some instances.
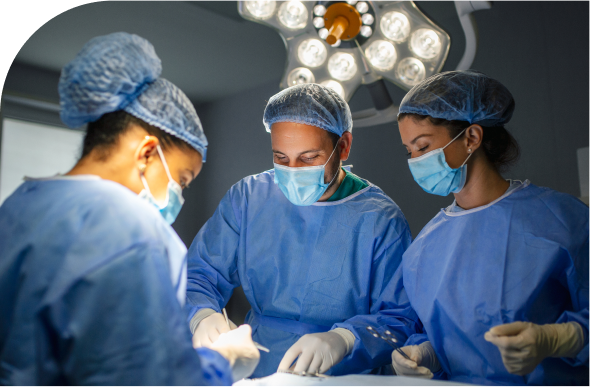
For individuals with early-stage liver cancer, surgery is often the best treatment option. A skilled liver cancer surgeon in Mumbai will assess liver function and ensure there is no spread before proceeding with surgery. If the liver is functioning normally, a portion of it may be removed based on the size, number, and location of the tumour.
Dr. Deepak Chhabra, a leading liver cancer doctor in Mumbai, performs partial hepatectomy (liver resection) to remove the affected portion while ensuring the remaining liver is sufficient for proper function. Depending on the case, a right or left hepatectomy may be performed for optimal treatment outcomes.
Cirrhosis or other conditions that impair liver function, the location of the tumor within the liver, or other health issues may prevent surgery to remove the tumor in some instances. Ablation is a method of local destruction used in these situations.
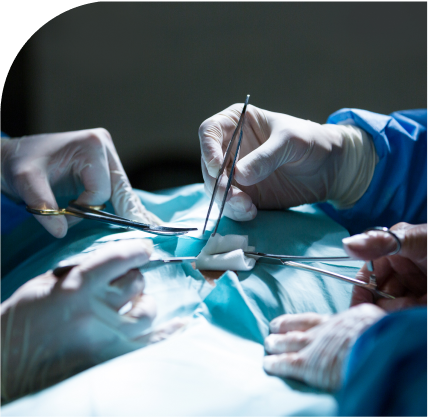
This sort of therapy gives the chemotherapy straightforwardly to the region of the liver that contains the disease. You may need to stay in the hospital for an extended period of time, depending on the drugs that were used. If you are unable to undergo surgery to remove your tumor, your doctor may suggest it. It is also sometimes used to shrink a tumor down to the size that it can be removed surgically later.

Dr. Deepak Chhabra is a consultant Surgical Oncologist with an extensive experience in cancer surgeries. He is has specialized in Hepato (Liver) -Biliary (Gallbladder) and Pancreatic Cancer Surgeries.
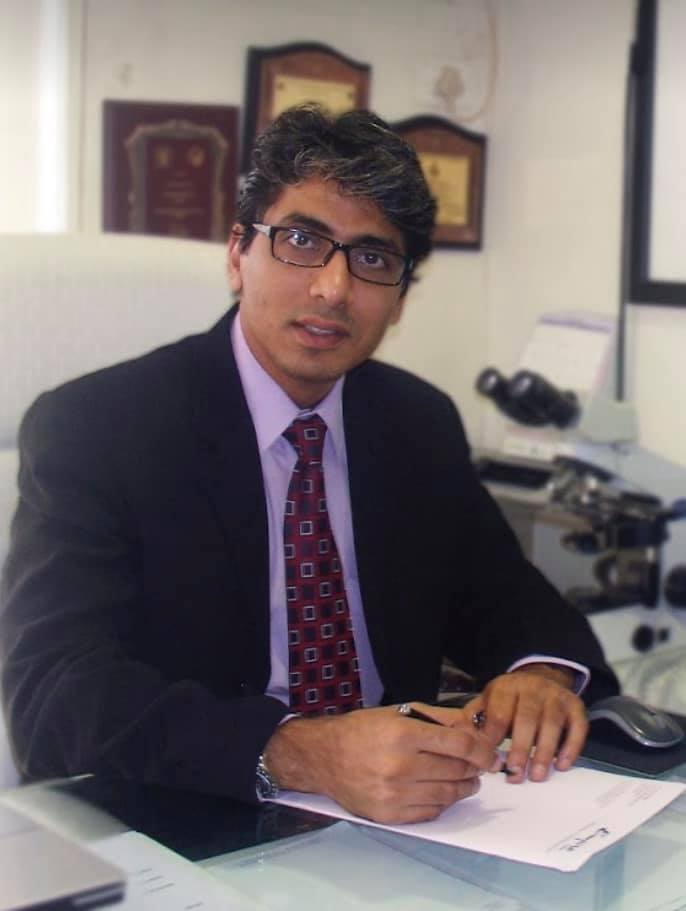

Take the first step towards your journey to wellness by scheduling an appointment with Dr. Deepak Chhabra, a trusted oncologist dedicated to providing compassionate care and personalized treatment plans.
Discover first hand accounts from patients who have experienced compassionate care and expert treatment at our clinic. Read their reviews to get to know their journey.
5 Out of 5 from 92 Reviews
